Scheduled Tasks
Scheduled tasks run your worker at specific times or intervals using cron expressions. Use them for background jobs like sending emails, cleaning up data, syncing external APIs, or generating reports.
Cron Syntax
OpenWorkers supports standard cron expressions with an optional seconds field.
5-field format (standard)
┌───────────── minute (0-59)
│ ┌───────────── hour (0-23)
│ │ ┌───────────── day of month (1-31)
│ │ │ ┌───────────── month (1-12)
│ │ │ │ ┌───────────── day of week (0-6, Sun=0)
│ │ │ │ │
* * * * *6-field format (with seconds)
┌───────────── second (0-59)
│ ┌───────────── minute (0-59)
│ │ ┌───────────── hour (0-23)
│ │ │ ┌───────────── day of month (1-31)
│ │ │ │ ┌───────────── month (1-12)
│ │ │ │ │ ┌───────────── day of week (0-6, Sun=0)
│ │ │ │ │ │
* * * * * *Examples
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
* * * * * | Every minute |
*/5 * * * * | Every 5 minutes |
0 * * * * | Every hour |
0 0 * * * | Every day at midnight |
0 9 * * 1 | Every Monday at 9:00 AM |
0 0 1 * * | First day of every month |
*/30 * * * * * | Every 30 seconds (6-field) |
0 */5 * * * * | Every 5 minutes at second 0 (6-field) |
Special characters
| Character | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
* | Any value | * * * * * (every minute) |
*/n | Every n units | */15 * * * * (every 15 min) |
n-m | Range | 0-30 * * * * (minutes 0-30) |
n,m | List | 0,30 * * * * (at 0 and 30) |
Scheduled Event
When your cron triggers, the worker receives a scheduled event with the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
scheduledTime | When the task was scheduled to run (Unix timestamp in milliseconds) |
ES Modules (recommended)
The modern syntax. Your handler receives event, env, and ctx as arguments.
export default {
async scheduled(event: ScheduledEvent, env: Env, ctx: ExecutionContext): Promise<void> {
console.log(`Running at ${new Date(event.scheduledTime).toISOString()}`);
// Access bindings via env
await env.DB.query("INSERT INTO logs (time) VALUES ($1)", [event.scheduledTime]);
}
}Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event | ScheduledEvent | Event object with scheduledTime |
env | Env | Object containing environment variables and bindings |
ctx | ExecutionContext | Execution context with waitUntil() |
Service Worker (legacy)
The older syntax using addEventListener. Still supported for backwards compatibility.
addEventListener('scheduled', (event: ScheduledEvent) => {
event.waitUntil(handleSchedule(event.scheduledTime));
});
async function handleSchedule(scheduledTime: number): Promise<void> {
console.log(`Running at ${new Date(scheduledTime).toISOString()}`);
// Access bindings via globalThis.env
await globalThis.env.DB.query("INSERT INTO logs (time) VALUES ($1)", [scheduledTime]);
}ScheduledEvent interface
interface ScheduledEvent {
scheduledTime: number;
waitUntil(promise: Promise<any>): void;
}Practical Examples
Daily cleanup
Delete old records every day at 3:00 AM.
0 3 * * *export default {
async scheduled(event, env, ctx) {
const cutoff = Date.now() - 30 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000; // 30 days ago
await fetch('https://api.example.com/records/cleanup', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${env.API_TOKEN}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ before: cutoff })
});
console.log('Cleanup completed');
}
}Hourly sync
Sync data from external API every hour.
0 * * * *export default {
async scheduled(event, env, ctx) {
const response = await fetch('https://external-api.com/data');
const data = await response.json();
await fetch('https://api.example.com/import', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
console.log(`Synced ${data.length} records`);
}
}Health check every 5 minutes
Ping your services and alert on failure.
*/5 * * * *export default {
async scheduled(event, env, ctx) {
const services = [
'https://api.example.com/health',
'https://app.example.com/health'
];
for (const url of services) {
try {
const response = await fetch(url, { method: 'HEAD' });
if (!response.ok) {
await sendAlert(env, `${url} returned ${response.status}`);
}
} catch (error) {
await sendAlert(env, `${url} is unreachable: ${error.message}`);
}
}
}
}
async function sendAlert(env, message) {
await fetch(env.SLACK_WEBHOOK, {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ text: `🚨 ${message}` })
});
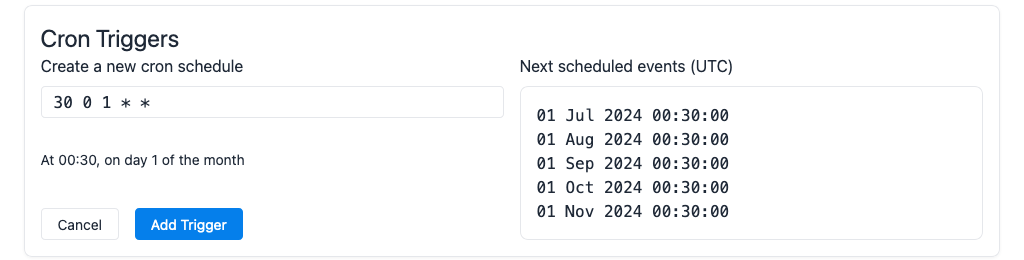
}Setting Up Cron Triggers
- Go to your worker in the dashboard
- Click on Cron Triggers
- Add a cron expression
- Save
Limits
Scheduled tasks have the same limits as HTTP requests:
| Resource | Limit |
|---|---|
| CPU Time | 100ms |
| Wall Clock | 60 seconds |
| Memory | 128 MB |
See Limits & Quotas for details.
Tips
- Use
ctx.waitUntil()to ensure async operations complete before the worker terminates - Log important milestones for debugging
- Set appropriate timeouts on external API calls
- Use secrets for API keys and tokens
- Keep tasks idempotent (safe to retry)